Anemia is a common health issue that affects our overall health, including our eyes. It’s important to know the visual signs of anemia to take action early. This article will cover the eye symptoms linked to anemia. We aim to help you spot and manage this condition.
Read interesting things at : vetocellacvgummies
Key Takeaways
- Anemia can show through signs like pale eyelids, yellow sclera, and vision changes.
- Spotting these signs early can help in treating anemia effectively.
- Age, gender, and diet can play a role in anemia and eye symptoms.
- See a doctor if eye symptoms don’t go away or get worse, as it could be serious.
- Eating a balanced diet with iron and making lifestyle changes can prevent and manage anemia eye problems.
Understanding Anemia and Its Impact on Eye Health
Anemia is a condition where there are fewer red blood cells or less hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries oxygen throughout the body. This shortage can affect eye health because the eyes need oxygen-rich blood to work right.
What is Anemia?
Anemia happens when the body can’t make enough red blood cells or when those cells don’t carry oxygen well. This can be from iron lack, chronic diseases, blood loss, or genetic issues. Not having enough oxygen can hurt many parts of the body, including the eyes.
How Anemia Affects the Eyes
- Impaired vision: Anemia can lead to less oxygen for the eyes, causing blurry vision, trouble focusing, and even temporary blindness.
- Eye fatigue and strain: The eyes may get tired and strained trying to work with less oxygen-rich blood.
- Dry eyes: Anemia can make the eyes dry and irritated, leading to discomfort and trouble making tears.
- Increased sensitivity to light: Some people with anemia might feel more sensitive to bright lights, which can be uncomfortable and disrupt their day.
Knowing how anemia affects the eyes is key to spotting eye problems early and getting help. Treating anemia can help manage eye issues and keep eyes healthy.
Pale Eyelids: A Common Sign of Anemia
One of the most recognizable signs of anemia is pale eyelids. This happens because there are fewer red blood cells. This means less oxygen-rich blood reaches the skin around the eyes. Knowing why this happens and how to spot it can help people get medical help fast.
Causes of Pale Eyelids
Pale eyelids in anemia come from not having enough hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. When there are fewer healthy red blood cells, the skin around the eyes looks paler. This is because it’s not getting enough oxygen-rich blood.
Several things can lead to pale eyelids anemia, including:
- Iron deficiency: This is a common cause of anemia. It leads to a lack of hemoglobin and pale eyelids.
- Blood loss: Losing a lot of blood can use up the body’s iron and cause checking for pale eyelids.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Not getting enough vitamins and minerals needed for making red blood cells can also cause pale eyelids.
How to Check for Pale Eyelids
It’s easy to check for pale eyelids to see if you might have anemia. Here’s how:
- Look at the inner lower eyelid: Pull down the lower eyelid and see the skin color. If it looks unusually pale or white, it could be a sign of anemia.
- Compare to normal skin tone: See if the eyelid skin is much lighter than the rest of your face or other skin. If it is, it might mean you have pale eyelids anemia.
- Notice any changes over time: If your eyelids keep getting paler or stay pale, you should see a doctor for help and treatment.
By watching for checking for pale eyelids and knowing why it happens, people can act fast to fight anemia. This helps keep them healthy and feeling good.
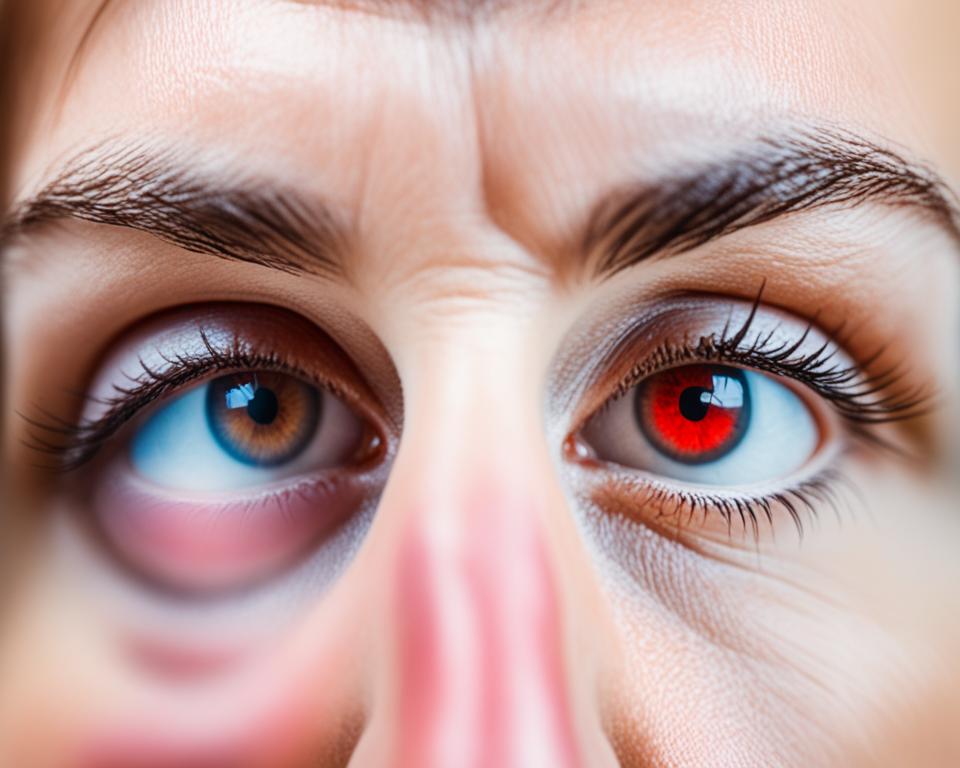
Yellow Sclera: A Potential Indicator of Anemia
A yellow color in the white part of the eye can signal anemia. This color comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of breaking down red blood cells. It’s a sign of yellow sclera anemia.
When the body can’t break down bilirubin, it builds up. This happens more in people with anemia. The bilirubin then goes into the sclera, making it look yellow.
- Anemia, a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin, can lead to yellow sclera.
- The yellow color is usually most seen in the morning and may lessen during the day.
- Other health issues, like liver disease or jaundice, can also turn the sclera yellow.
Yellow sclera doesn’t always mean the anemia is severe. The color change can vary by person and condition. If you see yellow in your eyes and it doesn’t go away, see a doctor for help.
“The yellow sclera is a telltale sign that something may be amiss with your health, and it’s important to pay attention to it.”
Knowing about the link between yellow sclera and anemia helps people get medical help faster. This can lead to better health and well-being.
Fatigue and Dizziness: Symptoms of Anemia
Anemia means you have fewer red blood cells or less hemoglobin than normal. This can make you feel very tired and dizzy. These symptoms happen because your blood can’t carry enough oxygen.
The Link Between Anemia and Fatigue
Feeling tired is a common sign of anemia. Without enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, your body can’t get enough oxygen. This makes you feel exhausted, even with simple tasks.
People with anemia often can’t keep up their energy all day. They might need to rest a lot or take breaks. This can make it hard to do daily tasks or be active.
Anemia and Dizziness
Anemia can also make you feel dizzy or lightheaded. This happens when your body can’t spread oxygen well. It can cause your blood pressure to drop, making you feel off balance.
This dizziness can be dangerous, as it raises the chance of falling or getting hurt. You might need to sit or lie down to avoid losing your balance. This makes everyday tasks even harder.
If you’re always tired or dizzy, see a doctor. They can find out why and help you get better. Getting the right treatment can boost your energy and improve your health.
| Symptom | Description | Potential Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Persistent feelings of tiredness and lack of energy | Reduced oxygen delivery to tissues due to low red blood cells or hemoglobin |
| Dizziness | Feelings of lightheadedness, unsteadiness, or vertigo | Temporary drop in blood pressure due to insufficient oxygen supply |
Shortness of Breath: An Overlooked Symptom
Many people don’t know that anemia can cause shortness of breath. When the body doesn’t have enough oxygen-rich blood, even simple tasks become hard. This sign is often missed but is key to knowing you need medical help.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you’re always out of breath, you should get medical advice. This could mean you have severe anemia or another condition that needs quick action. Look out for these signs to see a doctor:
- Shortness of breath during light physical activity or at rest
- Difficulty catching your breath or feeling like you’re gasping for air
- Shortness of breath that interferes with your daily routine or sleep
- Chest pain, dizziness, or a rapid heartbeat accompanying the shortness of breath
Don’t ignore these signs, as they could point to a serious issue with your anemia. Getting help early can greatly improve your health and prevent further problems.
Knowing how anemia and shortness of breath are linked helps you act fast to keep your health in check. If you keep having trouble breathing, don’t wait to talk to your doctor. They can give you a full check-up and the right treatment plan.
Rapid Heartbeat: A Sign of Oxygen Deprivation
One of the key symptoms of anemia often missed is a rapid heartbeat, or palpitations. This happens because your body tries to make up for fewer red blood cells that carry oxygen.
With anemia, your heart must work harder to move oxygen-poor blood around your body. This makes your heart rate go up, causing it to beat faster than usual. Rapid heartbeat is how your body tries to get more oxygen to your tissues and organs.
If you notice your heart beating faster suddenly or often, pay attention. A rapid heartbeat can show that your body is having trouble with anemia. It’s key to find out why you have anemia and fix it to get better.
“A rapid heartbeat is one of the most common symptoms of anemia, as the heart must work harder to pump oxygen-poor blood throughout the body.”
A rapid heartbeat can also be caused by other health issues, so seeing a doctor is a good idea. They can figure out what’s causing it and help you get the right treatment.
Knowing how anemia and a rapid heartbeat are linked helps you take steps to get better. Don’t ignore this sign – it might mean your body needs more help to work right.
Headaches and Irritability: Anemia’s Hidden Effects
Anemia means not having enough healthy red blood cells. It affects more than just the obvious symptoms. It can also hurt your mental and emotional health, causing headaches and irritability.
Managing Headaches and Irritability
Many people don’t see headaches and irritability as signs of anemia. They might think these are just normal feelings. But, these symptoms can really lower your quality of life. Luckily, there are ways to deal with them.
To fight anemia headaches, you need to fix the anemia itself. This could mean eating better, taking supplements, or seeing a doctor. Eating foods high in iron and drinking plenty of water can also help.
Handling anemia irritability takes a few steps. Fixing the anemia is key. Adding stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or exercise can help. Talking to friends, family, or a therapist can also be very helpful.
| Symptom | Causes | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia Headaches | – Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain – Reduced blood flow and pressure | – Treat underlying anemia – Maintain a balanced, iron-rich diet – Stay hydrated |
| Anemia Irritability | – Hormonal imbalances – Fatigue and low energy levels | – Address the anemia – Practice stress-reducing techniques – Seek emotional support |
Recognizing and handling anemia symptoms can lessen its hidden effects. It’s important to deal with both the physical and mental sides of anemia for a full recovery.
Anemia Symptoms Eyes: Recognizing Visual Signs
Anemia can show signs in the eyes that help spot the condition early. Knowing these signs lets people act fast and get the right medical help.
Pale eyelids are a common sign of anemia. This happens because there are fewer red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen around the body. As anemia gets worse, the eyelids may look very light or even white.
Yellow sclera, the white part of the eye, can also show anemia. The sclera may turn yellow, making the skin and eyes look yellow too.
- Pale eyelids
- Yellow sclera
- Dry eyes and vision changes
- Rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath
- Headaches and irritability
Anemia can also cause fatigue, dizziness, and a fast heartbeat. If you see these signs, seeing a doctor is key. They can figure out the cause and help you get better.
| Visual Sign | Cause | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Pale eyelids | Reduced red blood cell count | Indicates low oxygen levels in the body |
| Yellow sclera | Jaundice from anemia | Signifies potential liver or red blood cell issues |
| Dry eyes and vision changes | Anemia-related nutrient deficiencies | Suggests the need for dietary or medical interventions |
Spotting these signs of anemia means you can take steps to fix it. This can greatly improve your health and well-being.
Other Eye-Related Symptoms of Anemia
Anemia can cause more than just pale eyelids and yellow sclera. It can also lead to dry eyes and vision changes. These signs might not be easy to spot but they can affect your eye health.
Dry Eyes and Vision Changes
Anemia might make your eyes feel dry and uncomfortable. It can reduce tear production, making your eyes feel gritty or itchy. This can also make your vision blurry and make you sensitive to light.
Also, anemia can change how well you see things. People with anemia might find it harder to focus or read small print. They might struggle with seeing well at night or adjusting to different lighting.
These symptoms can make daily life harder. It’s important for people with anemia to know about these issues. If you notice any eye problems, you should see a doctor.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Dry Eyes | Reduced tear production leading to gritty, itchy, or uncomfortable eyes. |
| Vision Changes | Gradual decline in visual acuity, difficulty with night vision, and adjusting to changes in lighting. |
Risk Factors for Anemia
Anemia is a common condition that can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. Certain factors can make someone more likely to get anemia. We’ll look at age, gender, and diet as key factors.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender affect anemia risk. Women of childbearing age often need more iron because of menstruation and pregnancy. Older adults, especially those over 65, may face a higher risk due to poor nutrient absorption, chronic diseases, and some medicines.
Dietary Factors
What we eat greatly influences anemia risk. Eating too little iron from foods like red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and fortified cereals can increase risk. Conditions like celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disorders can also make anemia more likely.
To keep iron levels healthy and lower anemia risk, eat a balanced diet with:
- Red meat, poultry, and fish
- Legumes, such as lentils, beans, and peas
- Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale
- Fortified cereals and breads
- Dried fruits, such as raisins and apricots
Knowing the main risk factors for anemia helps people take steps to stay healthy. Making dietary and lifestyle changes can help keep iron levels right and improve overall health.
Diagnosing Anemia: Tests and Evaluations
If you think you might have anemia, it’s important to see a doctor. They will use tests to find out if you have anemia and what’s causing it. This helps you get the right treatment.
The first step is usually a simple blood test. This test checks your hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Low levels mean you might have anemia.
Doctors might order more tests to find the cause of anemia. These tests include:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to check red blood cell numbers and size
- Iron tests to see if you have enough iron
- Vitamin B12 and folate tests to check for deficiencies
- Reticulocyte count to measure new red blood cell production
In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy is needed. This test looks at how blood cells are made in the bone marrow. It helps doctors understand why you have anemia and how to treat it.
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Hemoglobin test | Measures the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells |
| Complete blood count (CBC) | Assesses the number and size of red blood cells |
| Iron tests | Determines iron levels in the body |
| Vitamin B12 and folate tests | Checks for deficiencies in these essential nutrients |
| Reticulocyte count | Measures the production of new red blood cells |
| Bone marrow biopsy | Evaluates the production of blood cells within the bone marrow |
By doing these diagnosing anemia and anemia tests, doctors can find out what kind of anemia you have and why. This lets them make a treatment plan just for you.
Treating Anemia: A Comprehensive Approach
When anemia is diagnosed, a detailed treatment plan is key. It includes dietary changes, supplements, and sometimes medical treatments. These steps help fix the root causes and ease symptoms.
Dietary Changes and Supplements
For many, changing their diet is a good first step. Eating foods high in iron like red meat, spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals can boost iron levels. Foods high in vitamin C also help the body absorb iron better.
If diet changes aren’t enough, doctors might suggest iron supplements. These can be tablets, liquids, or even infusions for severe cases. Always follow the dosage and watch for side effects.
Medical Interventions
For chronic or severe anemia, medical help is often needed. Doctors might prescribe erythropoietin (EPO) shots to boost red blood cell production. In some cases, blood transfusions are necessary to quickly increase blood levels and ease symptoms.
The best treatment for anemia depends on the cause, severity, and overall health. Working with a healthcare provider helps create a plan tailored to your needs. This way, you can get back to feeling well.

| Dietary Changes | Supplements | Medical Interventions |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Prevention: Maintaining Healthy Iron Levels
Preventing anemia is key to keeping your iron levels healthy. It’s not just about treating it. By eating foods high in iron and making lifestyle changes, you can lower your risk of getting anemia.
Eating an Iron-Rich Diet
Eating a diet full of iron is a great way to avoid anemia. Good iron sources include:
- Red meat, poultry, and seafood
- Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale
- Legumes, lentils, and beans
- Fortified cereals and bread
- Dried fruits, such as raisins and prunes
Try to eat these foods often to keep your iron levels up and prevent anemia.
Lifestyle Modifications for Anemia Prevention
Along with a diet full of iron, there are other lifestyle changes you can make to help your iron levels:
- Avoid drinking tea, coffee, or eating foods high in calcium with meals, as they can lower iron absorption.
- Exercise regularly to help your body make more red blood cells.
- Manage stress well, as too much stress can lead to iron deficiency and anemia.
- Stop smoking, as it makes it harder for your body to use iron well.
By eating well and making these lifestyle changes, you can prevent anemia and keep your iron levels where they should be. This is good for your overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
This article has shown you the eye symptoms of anemia. Now, you know how to spot these signs. This knowledge helps you take steps to keep your eyes healthy.
Spotting anemia early and getting the right treatment is key. By eating better, taking supplements, and seeing a doctor, you can fight anemia and protect your vision. The sooner you start, the better your chances of success.
Keep an eye out for signs like pale eyelids, yellow sclera, and changes in vision. These signs mean it’s time to see a doctor. By acting fast, you can start on the road to better eye health and clear vision.



